Category:MIG Welders: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 173: | Line 173: | ||
6. '''Put all tools away and clean the work area. ''' | 6. '''Put all tools away and clean the work area. ''' | ||
==Videos== | |||
[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CWoam95PVCE Havoc caused by a broken cylinder valve] | |||
[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ejEJGNLTo84 Mythbusters episode on gas cylinder rocketry] | |||
Revision as of 21:24, 6 February 2024
| Extra precaution required for welders. Training / Tool Testing is essential. See Welding Safety doc. | |
|---|---|
| Eye protection required! | ||
|---|---|---|
| MIG Welders | |
|---|---|
| General Info | |
| Make | Varied |
| Model | Varied |
| Serial | Unknown |
| Specs | n/a |
| Manual | |
| Asylum Info | |
| Location | Metal Shop |
| Rubric | n/a |
| Training | [https://www.artisansasylum.com/class-
catalog Tool classes] |
| Testing | [https://www.artisansasylum.com/tool-testing Tool
testing], or come to the shop on Tool Testing Night |
| Restrictions | red |
There are two models of MIG welders at Artisans Asylum:
Manuals are available in the Equipment Manuals Google Drive
Link to: Millermatic 212 Manual
Link to: Millermatic 252 Manual
Materials
Use for:
- Mild Steel ONLY
Do not use for:
- Galvanized
- Plated
- Painted
- Oiled
- Rusted
- Powder-coated
- Greasy
- Nasty
- Ugly
- Bad
Safety Hazards

| |
|---|---|
1. UV damage to eyes. Welding Helmet with shade 12 protection or darker is required.
2. UV burns on exposed skin. The rays from the arc can cause severe radiation burn (worse than sunburn.) Cover exposed skin.
3. Burns from flame, sparks, hot workpieces. Wear welding gloves, cotton clothing (no synthetics) and closed toe shoes.
4. Poisoning from breathing gases produced by welding. Use ventilation. Do not stick head in fumes. Respirator recommended.
5. Keep workplace clear of flammable materials including grease, oil, solvents, paper.
6. Electrocution if welder is mishandled. Do not weld near puddles of water on floor or work area.
* Various safety links to keep you awake at night:
ANSI - General Safety in Welding and Cutting
Operation Notes
- Solvent based metal cleaning should be done with Simple Green or other low-intensity cleaners.
- Abrasive cleaning methods are also appropriate.
- No brake cleaner. Brake cleaner contains chlorinated hydrocarbons that create phosgene gas when combined with UV light. Ventilation will not prevent poisoning.
MIG Welders Available:
- Millermatic 212 Auto Set - welds material from 22 gauge to 3/8 in (9/5mm) thick.
- Millermatic 252- welds material from 22 gauge to 1/2 in. thick.
The shop supplies 025, .030, and .035 inch copper coated steel filler wire.
- The MIG welders in the shop use a gas mixture of 75% Argon and 25% CO2. Purge lines after use.
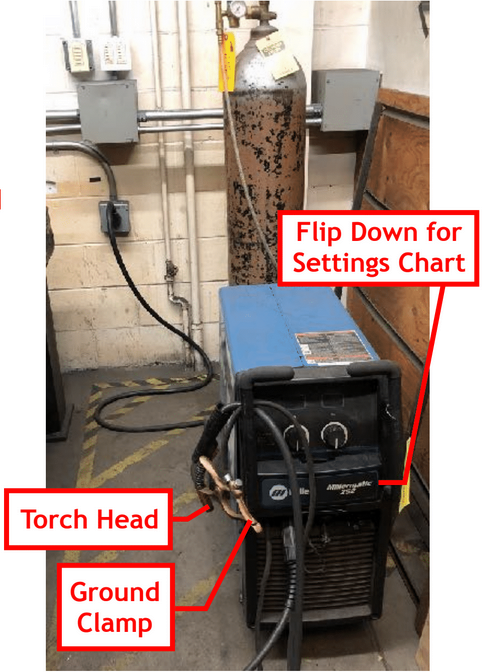
- To reduce spatter build-up, lightly coat Torch Head with Nozzle Anti-Spatter Gel. (Found in welding bays.)

| |
|---|---|
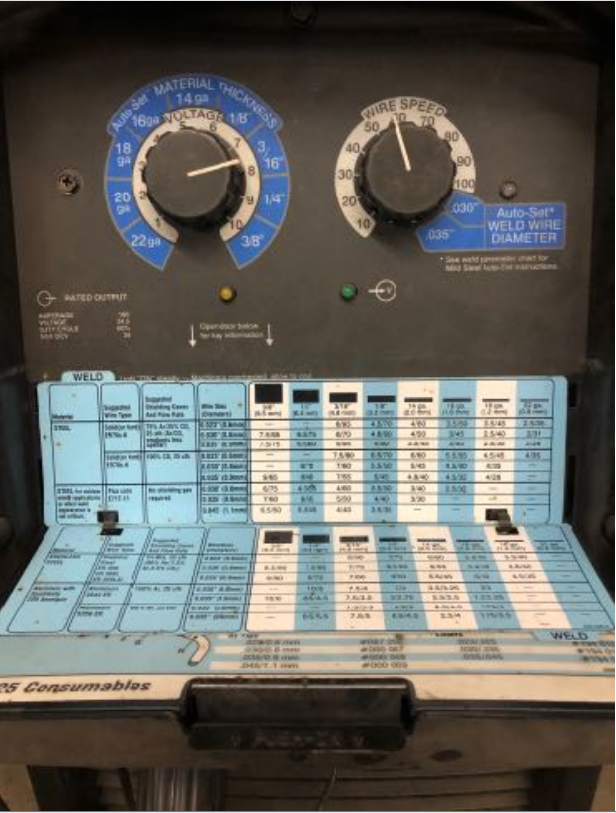
| Flip-Down Chart on the Millermatic 212 |
Set-up Procedure
1. Safety First
- Turn on welding bay ventilation.
- Remove flammable materials and water from welding area.
- Protect bystanders from the arc-flash, If you can’t depend on the protective vinyl
flaps on the welding bays, use welding screens
2. Attach the ground clamp to bare metal on the work table.
If workpiece is too large for the work table, clamp the workpiece.
3. Check to see if the welder has been shut down properly.
- Is the power shut off?
- Is the gas shut off at the cylinder valve?
- Have the lines been bled (is the working pressure at zero)?
4. Plug the machine in and turn it on.
5. Turn the gas on. If needed, adjust the pressure.
- SLOWLY crack the tank valve counterclockwise. Watch the regulator needle jump, and check that the needle has stopped moving before opening the valve (about half a turn).
This procedure lessens the impact of the initial jump in pressure on the regulator, reducing wear and tear.
- Hold the torch away from the workbench (more than 12 inches) and pull the torch trigger to start the gas cycle.
- Check the regulator dial to make sure the working gas pressure matches the recommendation listed on the shop tag attached to the regulator. Adjust if needed.
- Note: An inaccurate working pressure reading may occur if the welder has been shut down improperly by the previous user. Press the trigger on the Torch Head to lower the line pressure and reset the gauge.
6. Set the machine's voltage and wire speed.
- Take note of the wire size (written on the spool inside the machine) and the thickness of the workpiece.
- Start with the settings recommended on the flip down chart located on the front of the machine. Adjust the settings further as needed.
7. When welding, avoid tight loops or extra loops in the torch cord.
Extra looping will stress the feed mechanisms and may slow down the wire speed.
8. Dross may build up on the gas nozzle and/or contact tip while welding.
Clean as necessary using MIG pliers. Spare torch parts, including replacement contact tips, are kept in the Metal Shop’s supply cabinet.
Shut-Down Procedure
1. Shut off the gas at the source. Turn the cylinder valve clockwise.
2. Bleed the lines.
- Turn the wire speed down as far as it will go.
- Pull the torch trigger and wait for the regulator gauge to read zero.
3. Flip the machine's power switch to "off."
4. Turn the ventilation off if no one else is using the bays.
5. Loosely coil the torch cord and store on the machine.
6. Put all tools away and clean the work area.
Videos
Pages in category "MIG Welders"
The following 2 pages are in this category, out of 2 total.